Core Components
These are the core components of Paralus that provide core features including Zero Trust functionality. There are 5 core components of Paralus and each of them have their own repo.
Paralus
It exposes APIs that allows you to create and manage organization, projects, clusters, roles etc. This is at the heart of Paralus and responsible for authorization and authentication. It makes use of the following components for authentication & authorization:
- Kratos: Paralus makes use of Ory Kratos, an open source, cloud native Identity and User Management tool. It comes with its own deployment that consist of administrative user interfaces, hosted pages like login/registration, custom domain support, integration services and much more.
- Casbin: Casbin is a library that enforces policies and ensures that any actions like import clusters, create users, view audit logs etc. on Paralus system are done only by authorized users.
- Sentry: Sentry is an internal package that generates unique kubeconfig file for each user based on the policy definition. It provides an API endpoint to authenticate kubectl user requests and maps it to a user profile. It also takes care of roles, role bindings and Kubernetes related authentication related tasks.
To know more about Paralus, check out the Paralus GitHub Repo.
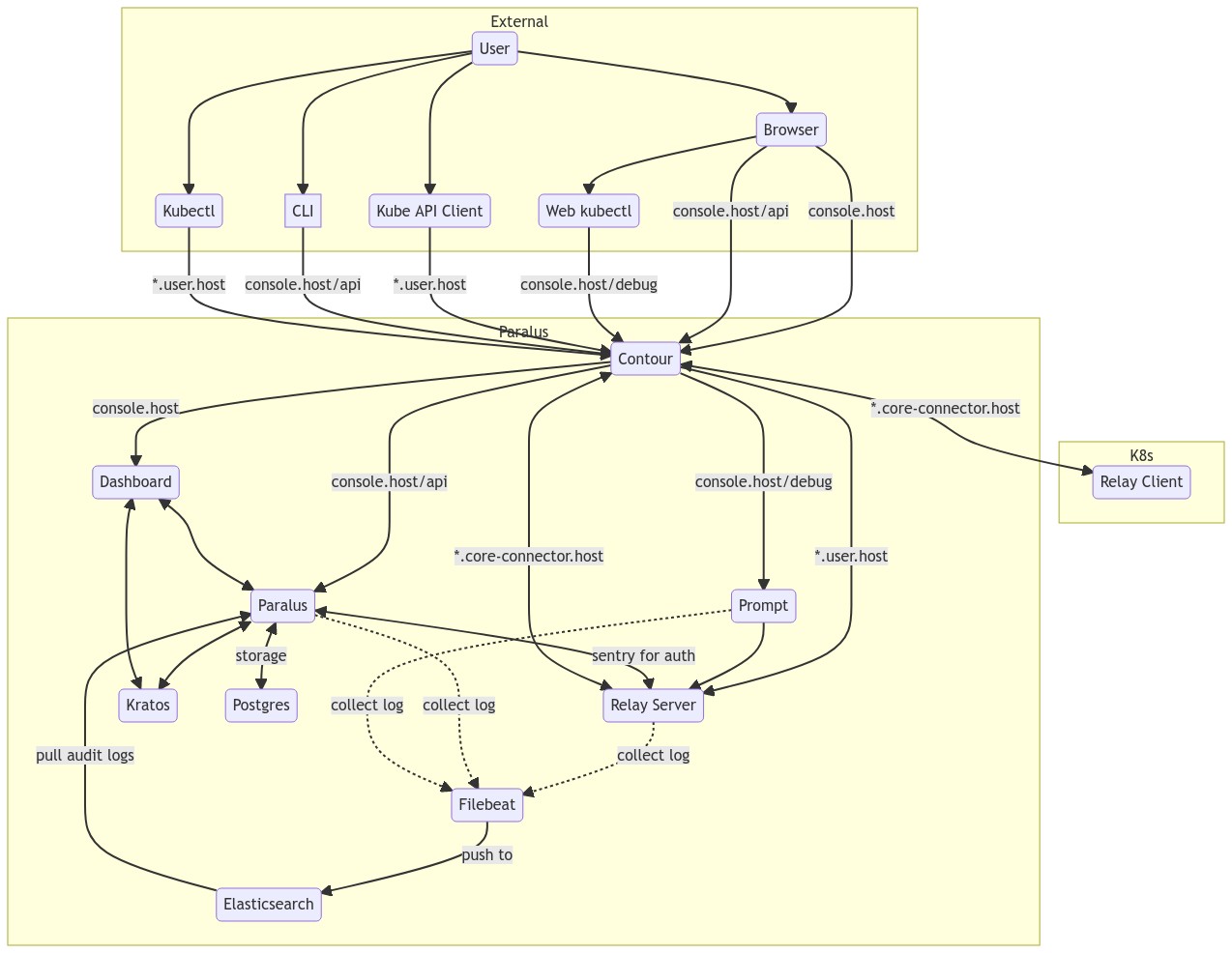
Relay
Relay is comprised of two parts, a Relay Server and a Relay Agent. Both of these work together allow the execution of kubectl commands on the target cluster.
Relay Server
It acts as a KubeAPI proxy and enforces access policies at the edge. It forwards only authenticated and authorized kubectl requests to the cluster. Accepts connections at *.user.domain-name and core-connector.domain-name endpoint. This involves TLS termination with client certificate validation using Paralus Certifying Authority. Upstream kubectl request to relay agents, establishes a long lasting channel between agents deployed in cluster using gRPC
Relay Agent
The Relay agent runs on the target Kubernetes cluster and establishes a gRPC channel with sentry service to register the cluster with Paralus. It connects to the Relay server and forwards authenticated/authorized kubectl requests to cluster Kube-API server. Based on the user policy, this creates a just-in-time service accounts.
To know more about Relay, check out the Relay GitHub Repo.
CLI
Paralus also comes with a command line tool called pctl that you can use to interact with Paralus. You can download the CLI binary, install it and access Paralus using the command line. Currently, pctl requires Paralus to be installed along with the dashboard. It doesn't work without that. It's part of our roadmap to make pctl run independently. It uses Cobra - an open source library that is used to develop CLI applications - under the hood.
We suggest you to read more about CLI. Check out the CLI GitHub Repo.
Dashboard
The dashboard is the primary way a user interacts with Paralus. It is an intuitive graphical user interface that allows the user to use all the features of Paralus. From creating projects, managing users and groups, importing clusters, the dashboard helps you to get things done quickly and easily.
Check out the Dashboard GitHub Repo.
Prompt
Paralus also provides a web based CLI tool called prompt. It allows the user to execute kubectl commands on designated clusters from the dashboard itself. It makes use of kubeprompt, an open source library which is an interactive kubernetes client featuring auto-complete.
Check out the Prompt Repo.
Read more about the miscellaneous components of Paralus.
