One of the best things that comes with Paralus is that it can be easily deployed to virtually any Kubernetes cluster. We have shown that in our previous blog posts where we deployed Paralus on GKE, Kind and even MicroK8s.
In this blog post, we'll take you through the steps to setup Paralus on Digital Ocean (DO) using a custom domain and import a local cluster into it. Let's get started!
Table Of Content:
- Pre Requisites
- Creating Digital Ocean Cluster
- Connecting to Digital Ocean Cluster
- Installing Paralus
- Configuring DNS Settings
Note: Before you start the installation process, do check out the pre-requisites for installing Paralus.
Pre Requisites
To setup Paralus on Digital Ocean there are a few things that need to done:
- A Digital Ocean account - you can register for a Free Digital Ocean account if you don't have one
- A Domain Name - with permission to manage DNS settings.
- Helm
We'll start with setting up a cluster on Digital Ocean, followed by deploying Paralus to it using helm charts. Once the installation is done, we'll configure the DNS settings for the domain for Paralus to work. After that we'll login to the Paralus dashboard and import a Kubernetes cluster that is running on a local laptop.
Creating Digital Ocean Cluster
Creating a Kubernetes cluster on DO is quite simple. DO offers just one type of Kubernetes cluster and not a variety of offerings like GKE, AWS or AKS. They provide two types of plans when it comes to Nodes - Basic and Professional plans, each of them offering a different configuration.
You need to choose the professional node plan with 3 nodes at the minimum for Paralus to run smoothly.
Login to your DO account and choose Kubernetes -> Create Kubernetes Cluster and provide details like cluster name, region, Kubernetes version, capacity etc.
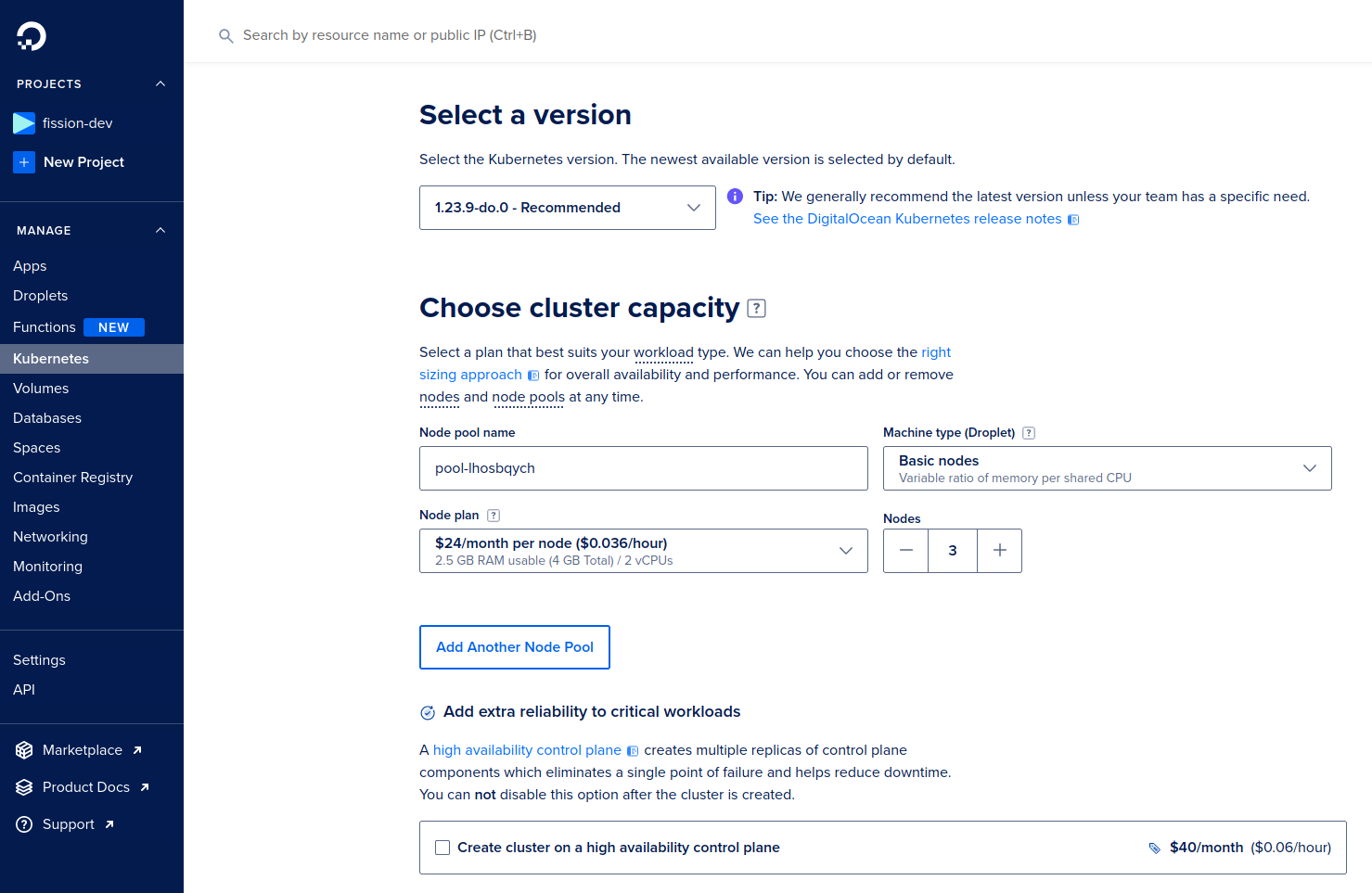
To know more about how to choose a plan or resize a Kubernetes cluster, check out this document.
Connecting to Digital Ocean Cluster
To connect to your newly created Kubernetes cluster there are two things that you need to do:
- Create API Token
- Configure doctl
1. Create API Token
You need to generate an API key to be able to access your Kubernetes cluster. You can follow this guide to create a personal access token.
2. Configure doctl
The next step is to configure doctl - a CLI tool provided by DO to interact with their API via command line.
We used a snap package to install the doctl package on our Ubuntu laptop.
Refer to doctl installation document to install it on different environment.
sudo snap install doctl
Create new context by providing the API token generated in the earlier step and switch to this newly created context
doctl auth init --context <NAME> followed by doctl auth switch --context <NAME>
Allow doctl to access the kube-config that will allow you to communicate with the Kubernetes cluster.
sudo snap connect doctl:kube-config
The next step is to configure a certificate to your kubectl configuration. You will get this certificate details after your cluster has been provisioned.
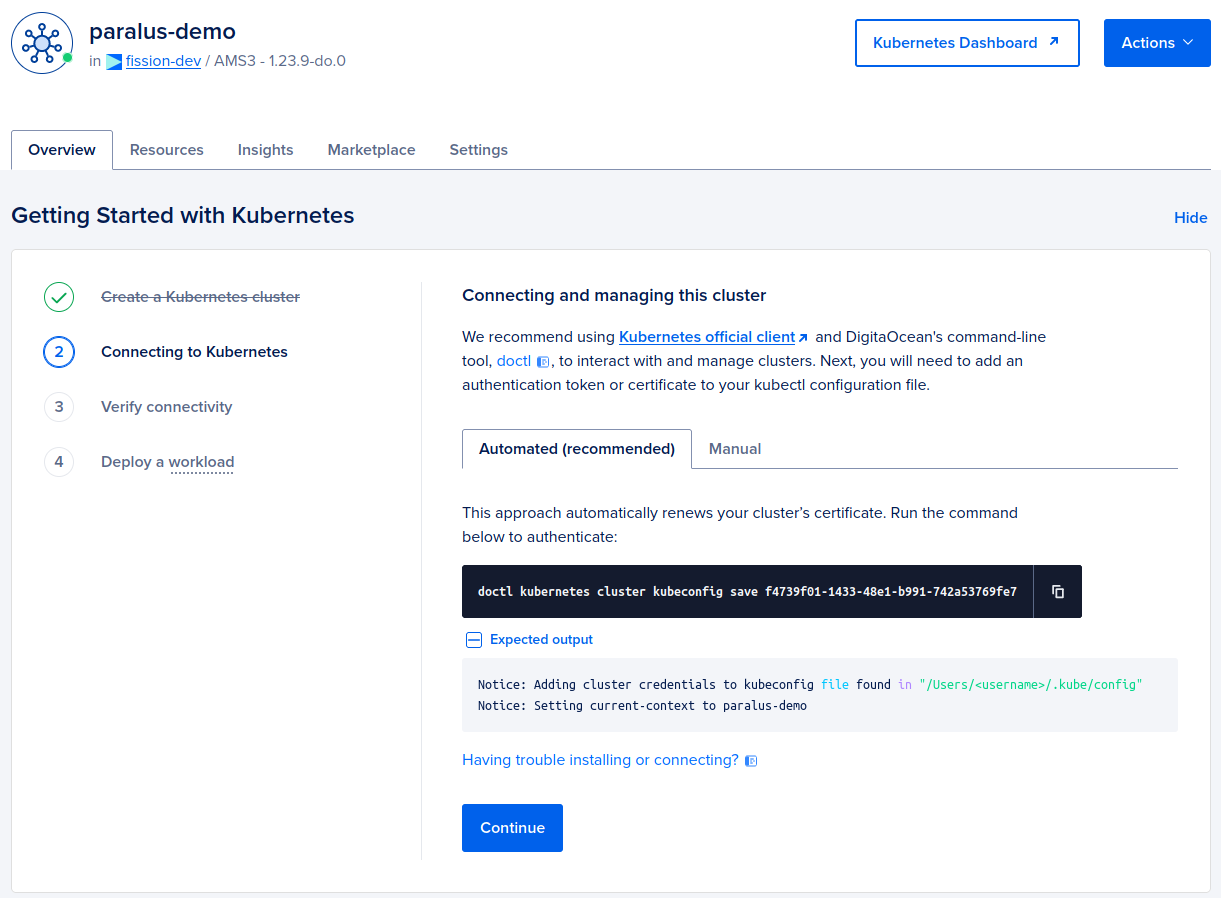
doctl kubernetes cluster kubeconfig save f4739f01-1433-48e1-b991-742a53769fe7
Notice: Adding cluster credentials to kubeconfig file found in "/home/atulpriya/.kube/config"
Notice: Setting current-context to do-ams3-paralus-demo
Once done, you can validate the connectivity using the following command
kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
pool-lhosbqych-7fomd Ready <none> 16m v1.23.9
pool-lhosbqych-7fomi Ready <none> 16m v1.23.9
pool-lhosbqych-7fomv Ready <none> 16m v1.23.9
At this point, you have successfully created a Kubernetes cluster & configured access to it using doctl. The next steps include installing Paralus and importing a local cluster on to it.
Installing Paralus
In the same terminal, you can follow the below steps to deploy Paralus to your DO cluster.
Add helm repo
helm repo add paralus https://paralus.github.io/helm-chartsInstall Paralus
helm install myrelease paralus/ztka \
-f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/paralus/helm-charts/main/examples/values.dev-generic.yaml \
--set fqdn.domain="chartexample.com" \
-n paralus \
--create-namespaceNote: If you're installing this in a production environment, please use values.yaml and configure the values mentioned here as required.
Note: Since v0.1.9, elasticsearch is an optional component. By default, Paralus will use database (Postgres) as the auditlog storage component. If you're doing a fresh install, below are the values.yaml file that you must pass during installation:
- Postgres (default): https://raw.githubusercontent.com/paralus/helm-charts/main/examples/values.dev-generic.yaml
- Elasticsearch: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/paralus/helm-charts/main/examples/values.elasticsearch.yaml
NAME: myrelease
LAST DEPLOYED: Mon Aug 29 17:29:54 2022
NAMESPACE: paralus
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
NOTES:
Access the application URL by running these commands:
Get the EXTERNAL-IP value using following command:
kubectl get service myrelease-contour-envoy -n paralus
Add DNS records of following domains such that it resolves to above address:
- console.chartexample.com
- *.core-connector.chartexample.com
- *.user.chartexample.com
Open http://console.chartexample.com in browser.
Note: If you are using a cluster with no load-balancer, then the address will be "<pending>".
If it is Kind or Minikube cluster, check out respective docs to get the external address.
You can view the recovery link for admin user by running the following command once all the pods are running:
kubectl logs -f --namespace paralus $(kubectl get pods --namespace paralus -l app.kubernetes.io/name='paralus' -o jsonpath='{ .items[0].metadata.name }') initialize | grep 'Org Admin signup URL:'
Note: It can take upto a few minutes before all the pods are running and you can access the dashboard. You can check the status using
watch kubectl get pods -n paralus
Configuring DNS Settings
Once the installation is complete, you need to first get the external IP address provided by the loadbalancer. You can do so by executing the following command:
kubectl get svc myrelease-contour-envoy -n paralus
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
myrelease-contour-envoy LoadBalancer 10.245.58.69 138.68.122.180 80:32722/TCP,443:32656/TCP 2m32s
It may take some time for the loadbalancer to assign the IP address.
Note down the EXTERNAL-IP address for the <releasename>-contour-envoy service.
Navigate to your domain's DNS setting page. The steps for changing DNS settings will vary based on your domain name provider.
While you are on your DNS Setting page, for the selected domain name, you need to add three A records. These will be based on the subdomains provided in the notes section post installation.
| Type | Address | Resolves To | TTL |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | console.chartexample.com | 138.68.122.180 | 1 Hour |
| A | *.core-connector.chartexample.com | 138.68.122.180 | 1 Hour |
| A | *.user.chartexample.com | 138.68.122.180 | 1 Hour |
Accessing The Dashboard
Paralus is installed with a default organization and an admin user. Hence, after installation, you need to set a password for the user. To do so, execute the command that you get after installing Paralus.
kubectl logs -f --namespace paralus $(kubectl get pods --namespace paralus -l app.kubernetes.io/name='paralus' -o jsonpath='{ .items[0].metadata.name }') initialize | grep 'Org Admin signup URL:'
Org Admin signup URL: http://console.chartexample.com/self-service/recovery?flow=de34efa4-934e-4916-8d3f-a1c6ce65ba39&token=IYJFI5vbORhGnz81gCjK7kucDVoiuQ7j
Note: The password recovery link generated while deploying Paralus is valid only for
10 minutes. For any reason if the link is expired, refer to our troubleshooting guide to re-generate the password reset link.
Access the URL in a browser, and provide a new password. In a new browser window/tab navigate to http://console.chartexample.com and log in with the following credentials:
- username:
admin@paralus.local- or the one you specified invalues.yaml - password:
<The one you entered above>
You'll be taken to the projects page where you'll see a default project.
Importing Existing Cluster
Everything in Paralus is grouped into Projects. Each project will have clusters, users and groups associated with it. Hence the first step it to create a new project.
Click on New Project to create a new project and then import a cluster in that project. The cluster we are importing is a minikube cluster hosted on my laptop.
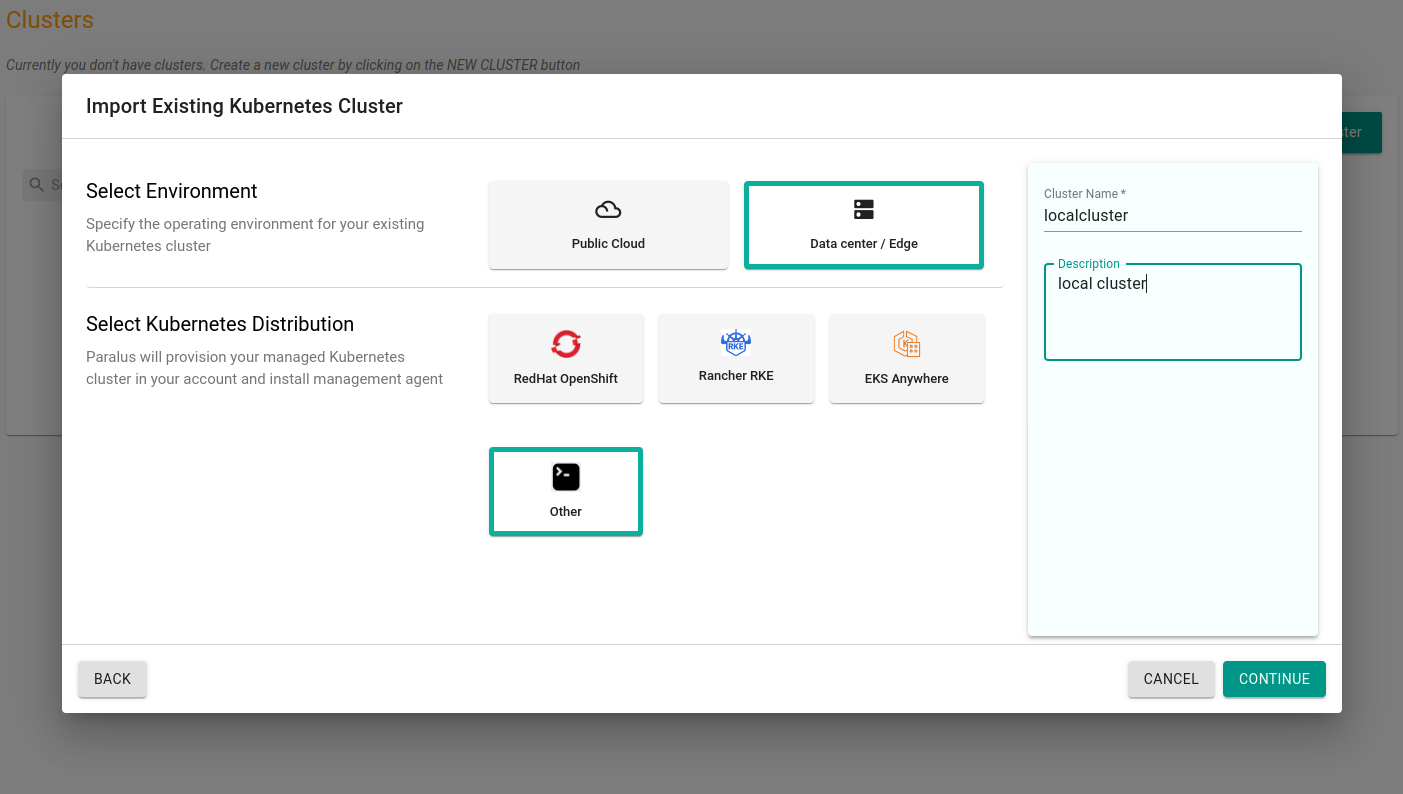
Click Continue and download the bootstrap yaml file by clicking Import Bootstrap YAML. This will download the YAML file that is required to connect your cluster with Paralus.
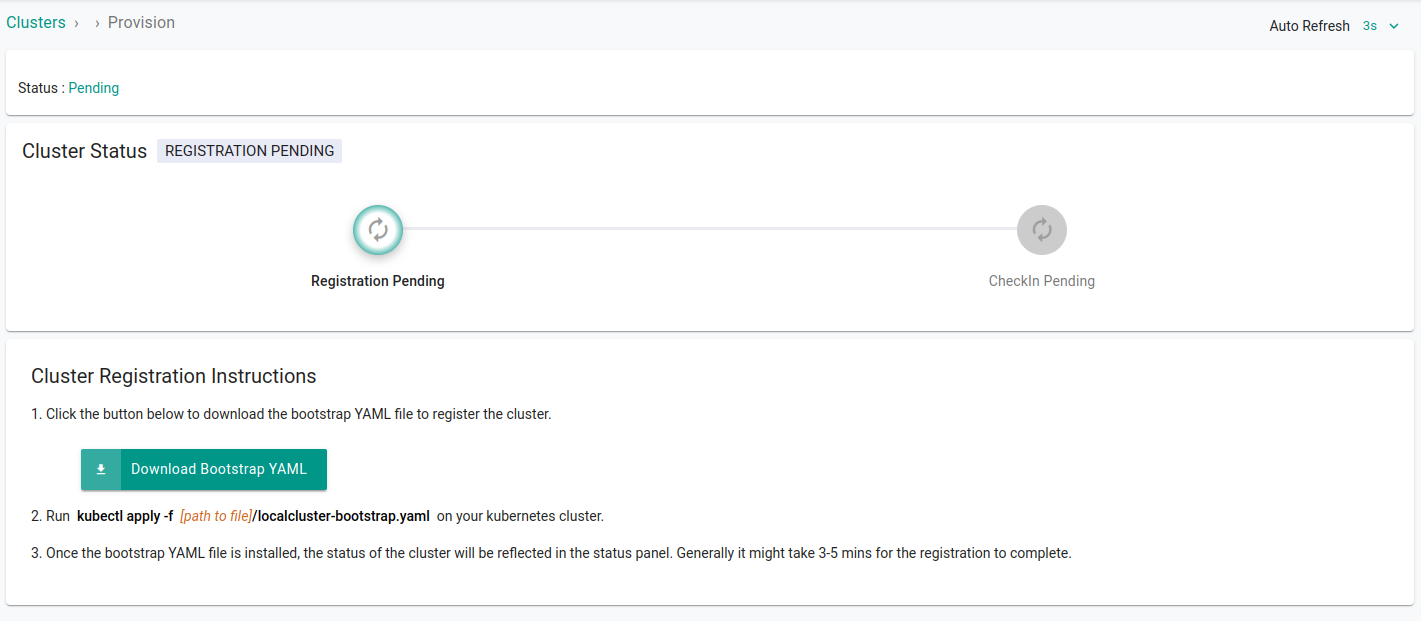
Apply the bootstrap configuration yaml file
kubectl apply -f mylocalcluster.yaml
Wait for the changes to take place. On the dashboard you will see that the cluster is imported successfully. It usually takes 3-5 minutes for the status to update.
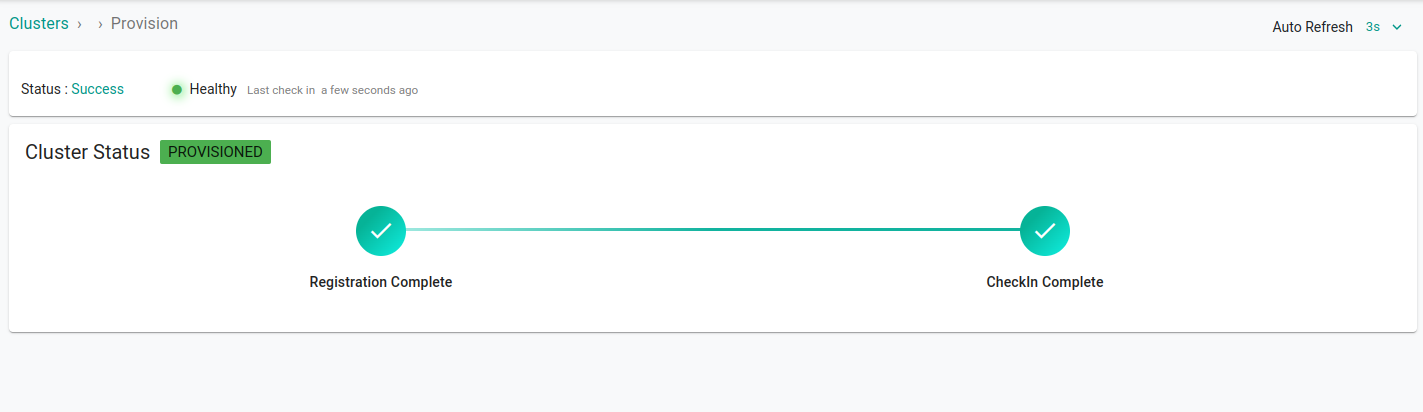
Select your newly imported cluster and click on kubectl to access the prompt and interact with your cluster from the dashboard.
A kubectl console will open in the bottom half of the screen, enter your kubectl commands to interact with your cluster.
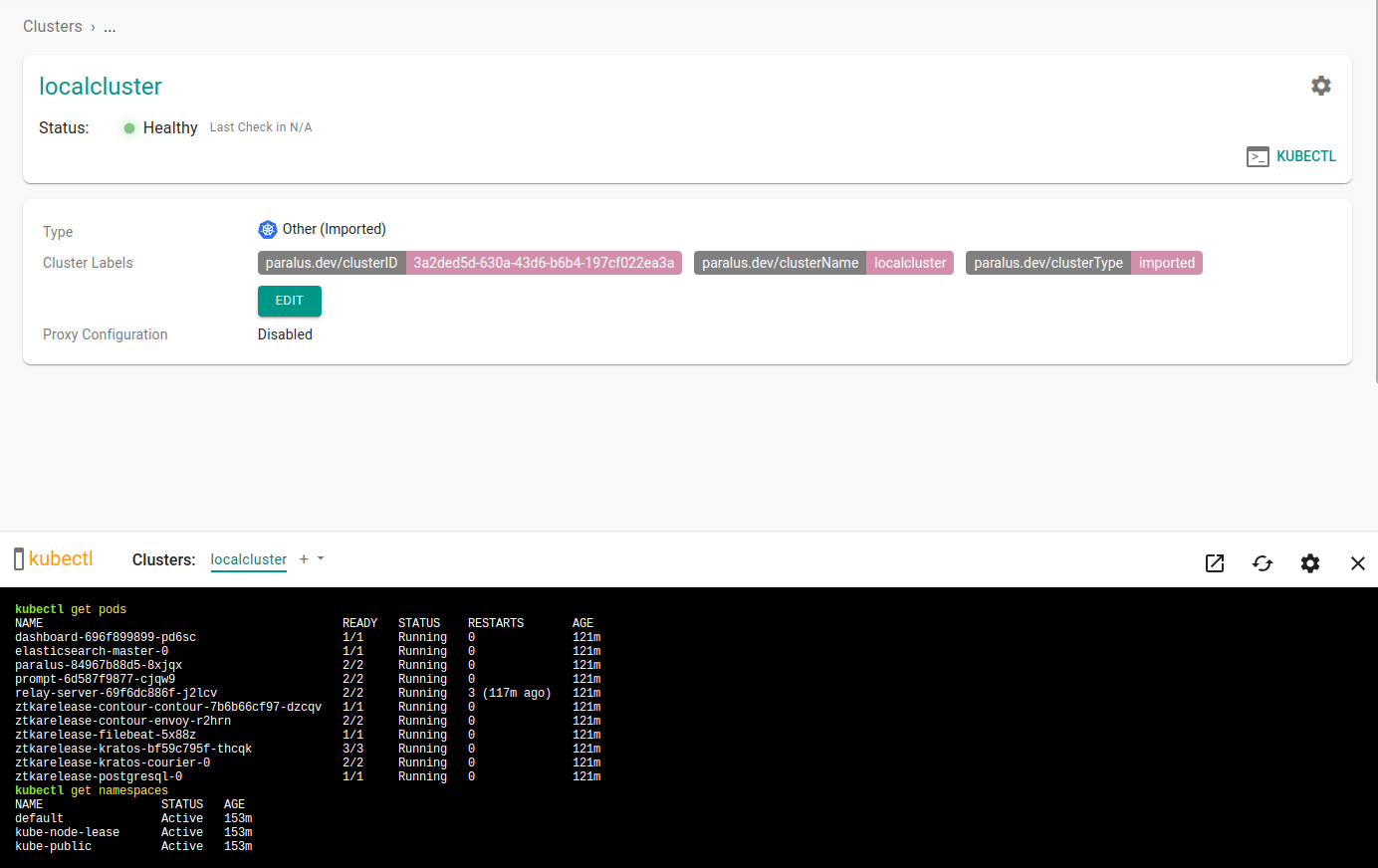
Congratulations! You've successfully deployed Paralus on Digital Ocean Kubernetes cluster and imported a local cluster.
Refer to our documentation to learn about various features of Paralus.
